Online applications for parameterized and customized design.
Here are the summarized general rules (RG) of design, categorized by common topics. The competitive and innovative advantages are highlighted in bold, and their application is illustrated with Figures or Tables.
RG-ME-02. Integrate information from 2D or 3D images into the design using computer tools with parametric models linked to medical criteria, market studies, or customer requirements [1].
Automated file and image processing reduces design time, rework, and the need for in-person appointments. Remote processing is facilitated through online platforms, local branches, or mobile applications, allowing for the generation and transmission of customer information for efficient remote processing [1].
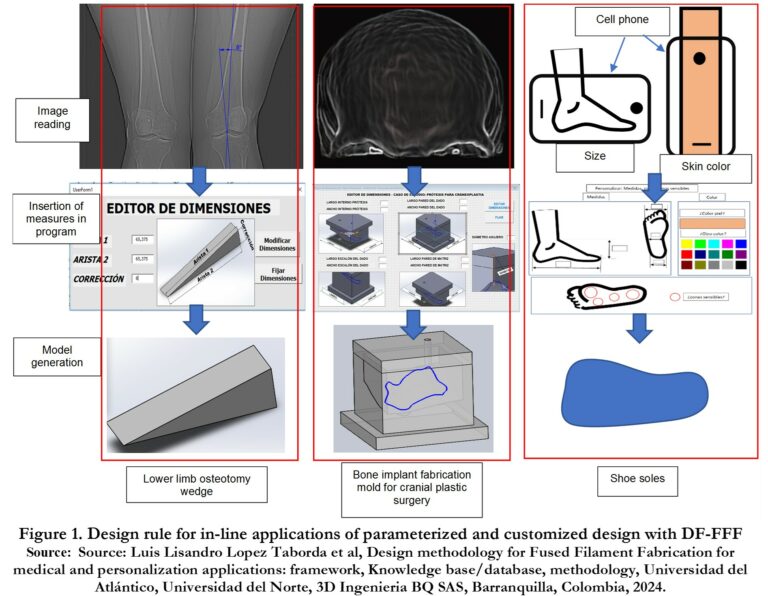
Figure 1 showcases examples of design applications, including parametric and customized wedge design for lower limb osteotomy, bone implant mold design for cranial plastic surgery, and individualized sole design [1].
The figure highlights the three stages (Top to bottom): image reading, insertion of measurement, and model generation. For the individualized sole, the client’s cell phone captures the image, measurements, and skin color [1].
References
[1] Luis Lisandro Lopez Taborda et al, Design methodology for Fused Filament Fabrication for medical and personalization applications: framework, Knowledge base/database, methodology, Universidad del Atlántico, Universidad del Norte, 3D Ingenieria BQ SAS, Barranquilla, Colombia, 2024.
